Resource Policies
IP addresses and AS numbers are shared resources, available for use by anyone who can demonstrate the need for them. APNIC policies ensure these resources are distributed fairly and consistently across the whole Asia Pacific region. Developments to policy are discussed in the Policy SIG.
Current policies
Use the links below to jump directly to a policy, or the “Current policies” link above, to view all current APNIC resource policies.
APNIC Policy SIG
The Policy SIG develops policies relating to Internet address resources by APNIC, NIRs, and ISPs within the Asia Pacific region.
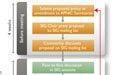
Policy Development
Learn how policies are developed by the Internet community
Policy proposals
View the proposals that may eventually become policy
APNIC drafts for public comment
View and comment on public drafts of documents incorporating policies that have successfully completed the policy development process.