I* organizations
The I* (I-star) group of organizations is a loose term to describe organizations that share responsibilities for coordinating the Internet technical infrastructure. APNIC collaborates with these organizations as part of the global Internet ecosystem.
The I* (I-star) organizations include the five Regional Internet Registries (RIRs), ICANN, ISOC, IETF, IAB, W3C and the regional associations of country code domain name registries.
Within their respective regions, RIRs such as APNIC provide services for the administration, management, distribution and registration of Internet number resources, specifically IPv4 addresses, IPv6 addresses, and Autonomous System numbers.
There are five RIRs:
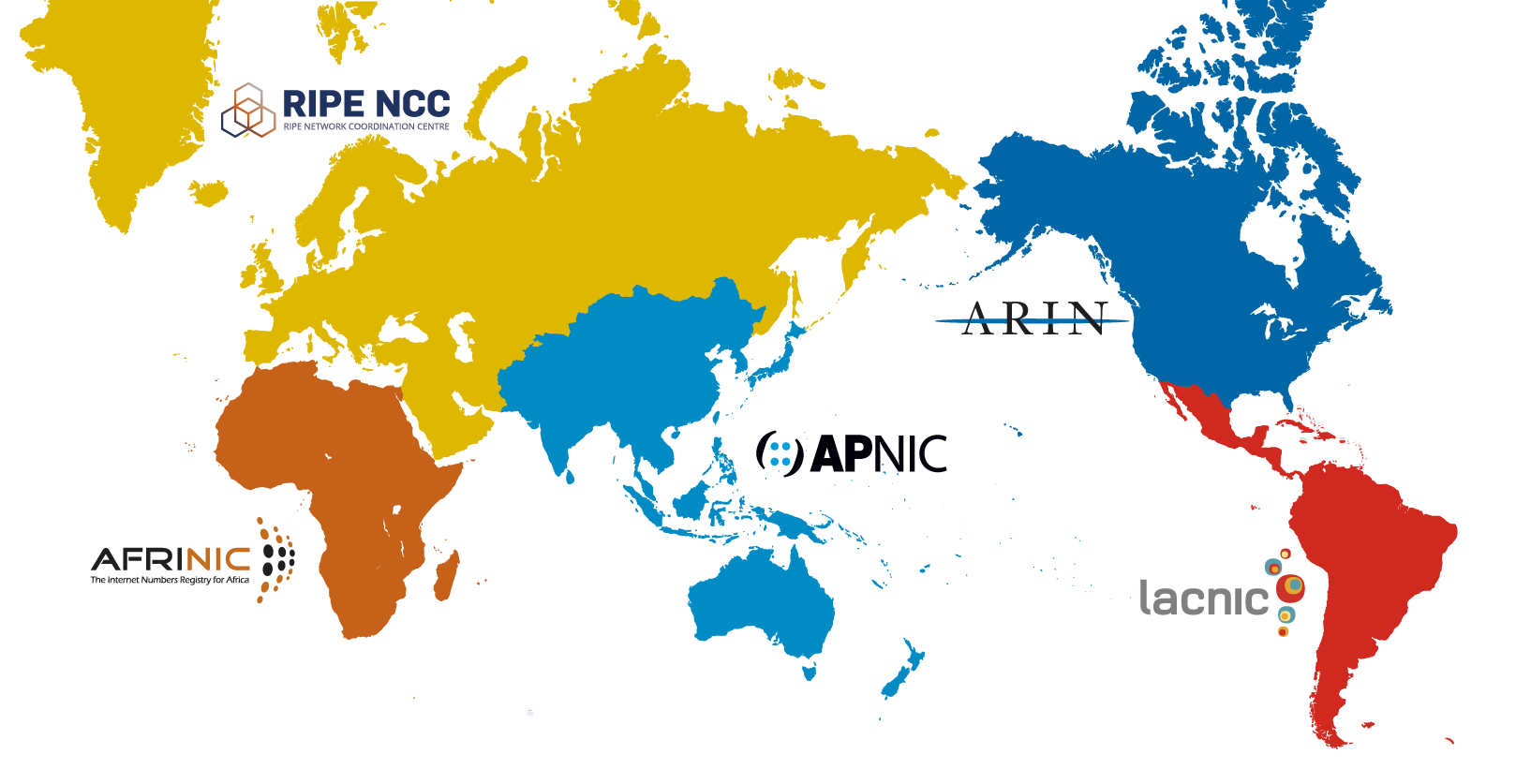
Services are based, in part, on policies the communities of each RIR develop in a multistakeholder, bottom up approach that is open to all interested parties. The Policy Development Process within each RIR region defines the way these policies are developed and adopted.

How RFC 9691 improves key rollover in RPKI Trust Anchors
New support for key transitions will give RIRs greater flexibility and improve long-term resilience of the RPKI.

APNIC community engagement on the ICP-2 Review
Many thanks to everyone who provided feedback on the draft RIR Governance Document. Read more about APNIC's engagement.
RIR community
The heart of the RIR system is the NRO, an umbrella organization to coordinate the activities of the five Regional Internet Registries (RIRs). The CEOs of each registry make up the Executive Council (NRO EC).
Number Resource Organization (NRO)
The Number Resource Organization (NRO) is a coordinating body for the five RIRs. The NRO contributes to an open, stable and secure Internet, through:- Providing and promoting a coordinated Internet number registry system
- Being an authoritative voice on the multistakeholder model and bottom-up policy process in Internet governance
- Coordinating and supporting joint activities of the RIRs.
The CEOs of each registry make up the Executive Council (NRO EC).
NRO Number Council
Three individuals are appointed to the Number Council (NC) from each of the Regional Internet Registry regions.
The RIRs are free to select these members in any way they see fit. The members of the NRO NC perform the functions of the ICANN Address Supporting Organization Addressing Council (ASO AC).
Read more about the NRO NC election.

Statement from the Number Resource Organization regarding AFRINIC elections
Guest Post: The NRO fully supports ICANN's efforts to bring transparency and accountability to the AFRINIC election process.

Nominations now open for NRO NC Election 2025
You have until 10 August 2025 to submit a nomination for the seat open for election on the NRO NC.
The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) is the international organization responsible for the management and oversight of the coordination of the Internet’s domain name system and its unique identifiers such as IP addresses. ICANN oversees the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA).

Consultation on Draft ‘Governance Document for the Recognition, Maintenance, and Derecognition of Regional Internet Registries’
Share your feedback on the 'RIR Governance Document'. The consultation period is open from 14 April to 27 May 2025.

Event Wrap: ICANN 82
Geoff Huston gave two presentations and Joyce Chen participated as a panellist at the ICANN 82 Community Forum, held from 8 to 13 March 2025 in Seattle, Washington.
ASO
The Address Supporting Organization (ASO) is one of three ICANN Supporting Organizations. The purpose of the ASO is to review and develop recommendations on IP address global policies and to advise the ICANN Board on IP addressing related matters. Since 2004, the NRO Number Council performs the role of the ASO within ICANN.

Nominations now open for NRO NC Election 2025
You have until 10 August 2025 to submit a nomination for the seat open for election on the NRO NC.

APNIC community engagement on the ICP-2 Review
Many thanks to everyone who provided feedback on the draft RIR Governance Document. Read more about APNIC's engagement.
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is one of the Internet’s oldest institutions, with its activities dating back to the 1970s. Today the IANA functions are provided by ICANN affiliate Public Technical Identifiers (PTI). PTI’s various activities can be broadly grouped in to three categories:
- Domain names – IANA manages the DNS root, the .int and .arpa domains, and an IDN practices resource
- Number resources – IANA coordinates the global pool of IP and AS numbers, providing them to RIRs
- Protocol Assignments – PTI manages the number systems of Internet protocols in conjunction with standards bodies
Find out more about the IANA oversight transition.

New IPv6 address block
APNIC extends its IPv6 resources with a second /12 allocation from IANA.

New RDAP profile to improve cross-RIR consistency
The NRO recently registered an RDAP profile with IANA for the RIR community.
The Internet Society (ISOC) is a non-profit organization, founded in 1992, dedicated to ensuring the open development, evolution, and use of the Internet for the benefit of people throughout the world. Its purpose is to provide leadership in Internet related standards, education, and policy.
![Banner image for [Podcast] Pulse Internet Measurement Forum at APRICOT 2025: Part 2 article.](https://blog.apnic.net/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/Generated-Image-March-17-2025-8_25AM.png.jpeg)
[Podcast] Pulse Internet Measurement Forum at APRICOT 2025: Part 2
The second PING recording from the first Pulse Internet Measurement Forum held during APRICOT 2025, featuring Amreesh Phokeer, Beau Geiskens, Doug Madory, and Lia Hestina.

Recapping PIMF Malaysia: 11 views on Internet Resilience
Guest Post: Mapping cables, measuring locally, security, security, security, and more from the first Pulse Internet Measurement Forum.
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is a large, open, international community of network designers, operators, vendors, and researchers who are interested in the evolution of Internet architecture and its smooth operation. The IETF is open to any interested individual. The technical work of the IETF is carried out in its working groups, which are organized by topic into several areas (for example, routing, transport, security, and more). The IETF holds meetings three times a year, however much of the work is handled via mailing lists.
![Banner image for [Podcast] DELEG: Changing the DNS engine in flight again article.](https://blog.apnic.net/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/Screenshot-2025-05-27-at-10.10.59%E2%80%AFam.png)
[Podcast] DELEG: Changing the DNS engine in flight again
Geoff Huston discusses the new IETF DELEG Working Group activity, which is looking to change how zones are delegated in the DNS protocol.

DNS at IETF 122
A roundup of new documents, current work, and new work from DNSOP.
The Internet Architecture Board (IAB) is both an IETF committee and an ISOC advisory body.
It is responsible for architectural oversight of IETF activities, Internet Standards Process oversight and appeal, and the appointment of the RFC Editor.
The IAB is also responsible for the management of the IETF protocol parameter registries.
A Country Code Top-Level Domain (ccTLD) is a two-letter top-level domain specifically designated to a particular economy, sovereign state, or autonomous territory.
The implementation of ccTLDs was started by IANA, which maintains a database that contains authoritative information relating to ccTLDs. Creation and delegation of ccTLDs is described in RFC 1591, corresponding to ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 country codes. To determine whether new ccTLDs should be added or not, IANA follows the provisions of ISO 3166 – Maintenance Agency.
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) develops standards and guidelines to help everyone build a web based on the principles of accessibility, internationalization, privacy and security.
